應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)(8位)八核心平行處理單晶片 (FPPA) 介紹 ,FPPA 架構(gòu)介紹,FPPA 產(chǎn)品特色,內(nèi)建硬體的即時(shí)作業(yè)系統(tǒng),FPPA 暫存器說(shuō)明
應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)FPPA 架構(gòu)介紹
應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)FPPA 產(chǎn)品特色
應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)內(nèi)建硬體的即時(shí)作業(yè)系統(tǒng)
應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)FPPA 暫存器說(shuō)明
應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)FPPA 軟體規(guī)劃
應(yīng)廣單片機(jī)FPPA 指令介紹
八核心單晶片有什么優(yōu)點(diǎn):
相信許多研發(fā)人員都有選擇 MCU 的痛苦經(jīng)驗(yàn), 選這顆 MCU 少個(gè) UART,選那顆 Timer 又不夠,就算選好了 MCU,寫(xiě)多功 (Muti-Task)的軟體才是真正痛苦的開(kāi)始.
應(yīng)廣科技(Padauk )八核心平行處理單晶片F(xiàn)ield Programmable Processor Array, 以下簡(jiǎn)稱“FPPA”,利用八核心平行處理可一次解決軟體“Muti-Task” ,“Timer” 和MCU 所需的各種周邊的困擾 .有八顆MCU 平行處理,不用再煩惱多工軟體,有八顆MCU 平行處理等于有八個(gè)Timer,不用再煩惱Timer 不夠,有八顆MCU 平行處理,拿幾顆來(lái)寫(xiě)UART,I2C,SPI ,PWM 等周邊就不用再煩惱介面不夠.
FPPA 架構(gòu)介紹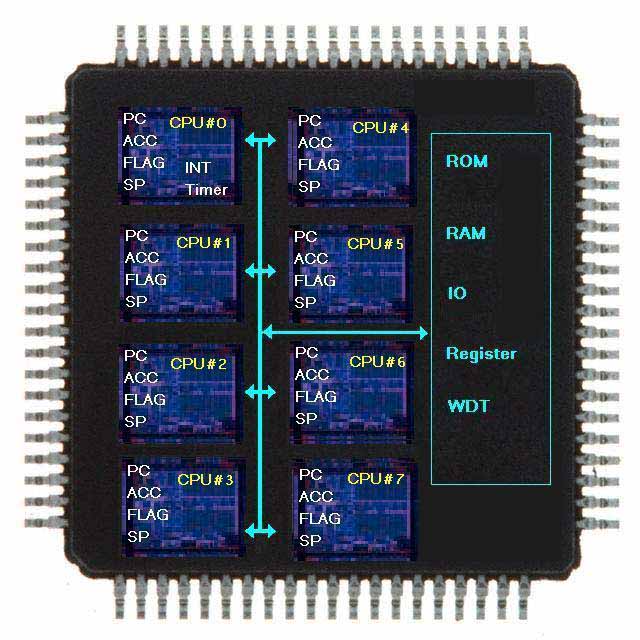
如上圖所示
基本上應(yīng)廣科技(Padauk )的FPPA, inside 了8 顆RISC type 1T 的MCU, 除了每顆MCU 有自己的Flag ,PC counter, Stack pointer, Accumulator 外,其余的ROM,RAM,IO 等是共用的 .故每一MCU 都可隨時(shí)監(jiān)控其他MCU 的狀況.(MCU#0 還多了16bit 的timer & 中斷管理可處理I/O中斷和內(nèi)部中斷).
8 顆MCU 是平行處理,且每個(gè)I/O 都可設(shè)為input 或output 或pull-hi 或open-drain,故可用軟體去控制I/O寫(xiě)各種周邊介面, 如I2C, UART,PWM,SPI 等非常有彈性(如MCU#0 寫(xiě)UART, MCU#1寫(xiě)I2C, MCU#2 寫(xiě)PWM 等,幾乎沒(méi)有限制.) 軟體去作SOC 周邊功能,故成本很有競(jìng)爭(zhēng)力,和彈性,不會(huì)受 限一般MCU 原廠所開(kāi)的IC 規(guī)格.
除了 一般 MCU 的指令外, 還有 類似 FPGA 才有 I/O 指令,對(duì) I/O 的處理特別精簡(jiǎn)和有效率.可取代部分的 PAL/GAL/FPAG 等邏輯合成電路.
產(chǎn)品特色 Features
內(nèi)建 8 顆 RISC type 平行處理,多核心 CPU 矩陣 (Field Programmable Processor Array“FPPA”).
內(nèi)建硬體的即時(shí)作業(yè)系統(tǒng) (hardware RTOS).
97 個(gè) 1T RISC type 功能強(qiáng)大的指令. (不同系列,指令略有增減)
支援 C/Assembly language/Macro 程式語(yǔ)言.
可自由規(guī)劃每一 MCU 的堆疊(stack pointer) 深度.
支援12bitx8ch ADC.
彈性方便的位元操作指令 (Bit-manipulation).
全部的資料記憶體都可用指標(biāo)定址 (index pointer addressing).
可自由規(guī)劃每一 MCU 的程式空間 ( OTP program memory).
每一 I/O 都可彈性定義為 input 或 output或 pull-hi或 open-drain.
內(nèi)建高速/慢速 RC振蕩器.
獨(dú)家的 intra-FPP handshaking指令,每一 MCU 可控制其他 MCU 的程式指標(biāo) (program counter).
獨(dú)家的內(nèi)部中斷,MCU#1 – MCU7 可發(fā)出中斷需求,讓 MCU#0當(dāng)中斷優(yōu)先處理.
獨(dú)家的 “wait0”, “wait1” 指令,對(duì) IO 的處理特別精簡(jiǎn)和有效率.
獨(dú)家的 “delay x” (x 0 – 255)指令,可直接 delay x 的 system clock.
內(nèi)建硬體的即時(shí)作業(yè)系統(tǒng) (hardware RTOS)
FPPA 最多可有8 顆MCU 同時(shí)平行處理, FPPA 有一“pmode”指令可調(diào)整每一MCU 的速度,FPPA 根據(jù)“pmode”由硬體強(qiáng)制去分配的每一MCU 的bandwidth 來(lái)完成類似軟體RTOS 的功能( 如下表),完全不用寫(xiě)軟體的RTOS.
| pmode | FPP0 | FPP1 | FPP2 | FPP3 | FPP4 | FPP5 | FPP6 | FPP7 |
| 0 | 1/2 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 |
| 1 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 |
| 2 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 |
| 3 | 1/2 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | ||||
| 4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/8 | |||
| 5 | 1/16 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | |
| 6 | 1/16 | 1/2 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 |
| 7 | 1/8 | 1/2 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 |
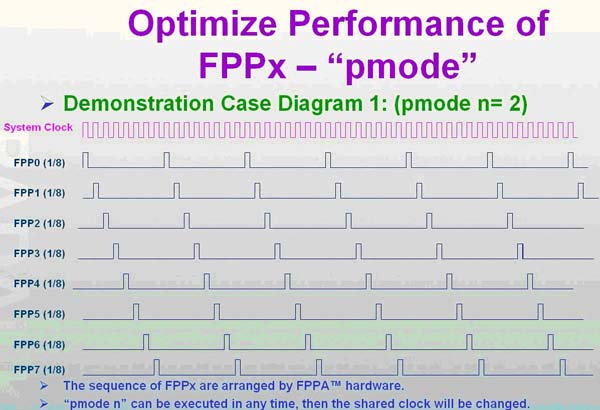
如下圖為 pmode =2 , 平均每一 MCU 分配 1/8 system clock
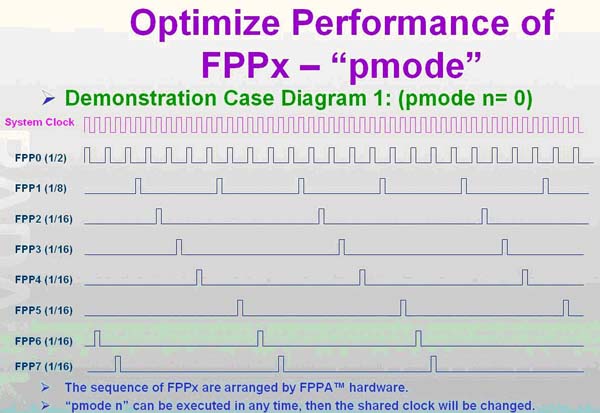
下圖為 pmode=0 ,FPP#0 = 1/2 system clock, FPP#1 = 1/4 system clock, FPP#2-FPP#7 = 1/16 system clock ,每個(gè) FPP 的 cycle 如下
FPPA暫存器 (Registers) 說(shuō)明
|
PPA 共有33 個(gè)暫存器(不同系列暫存器略有不同),其中address 0x10 – 0x32 各為I/O Port A – Port E 的控制暫存器,故真正要注意的register 只有13 個(gè),不 像其他MCU,周邊控制(如PWM,I2C,UART 等)的register 就好幾拾個(gè),故FPPA 很容易學(xué)習(xí)U. 13個(gè)register 中比較容易引起誤解,或datasheet 描述不易理解的地方特別提出說(shuō)明.
“sp” & “flag”: 由于 FPPA 有8顆 MCU,故每一 MCU 看到的 “sp” & “flag” 的值是不一樣的值.
“fppen”: 由于 FPPA 有8顆 MCU,但并不是每個(gè)應(yīng)用 8 顆 MCU 都要去 enable, 故可用 “fppen” register 去控制那些 MCU 需要 enable.
gdio”: register “gdio” 可以做下列二種應(yīng)用
當(dāng)warm-boot 或cool-boot的判斷用:由于FPPA 開(kāi)機(jī)或reset 時(shí), “gdio” 的值不會(huì)去變更,故程式執(zhí)行中可故意寫(xiě)入一個(gè)值給“gdio”,而在程式開(kāi)始的地方 去判斷“gdio” 的值是否為程式執(zhí)行中所寫(xiě)入的值即可判斷MCU 是否是第一次開(kāi)機(jī)或是reset 再開(kāi)機(jī).
讓MCU & MCU 間的溝通更有效率:“wait0” 和“ wait1” 指令除了可對(duì)I/O 處理外, 也可對(duì)“gdio” 暫存器處理, (Ex.: “wait0 gdio.x”) , 例如在MCU#1 中把“gdio.x” 設(shè)為0 或1, MCU#2 用“wait0” 或“wait1”指令去做條件的判斷亦可達(dá)到MCU#1 和MCU#2 之間的溝通 .
FPPA 軟體規(guī)劃
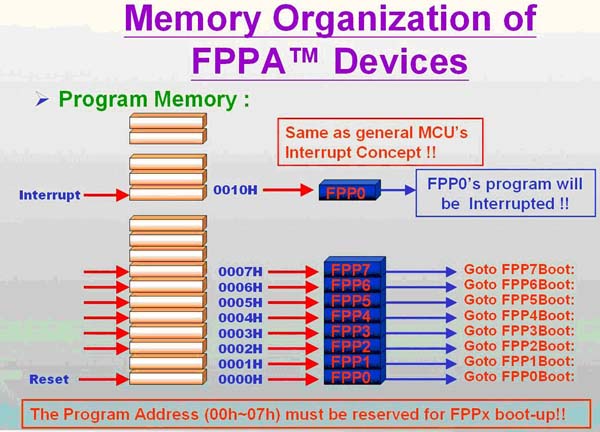
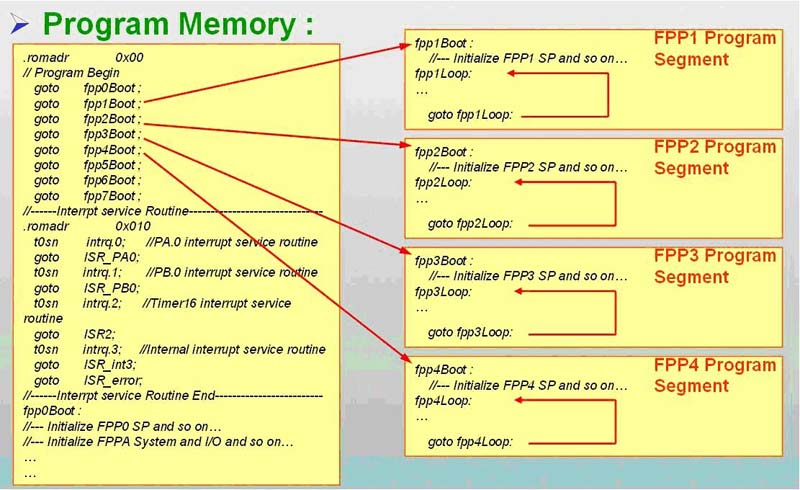
如上圖所示,和大多數(shù)的MCU 一樣,FPPA 也有所謂“中斷向量表”的概念,只是一般MCU 的中斷向量是“中斷副程式” 的進(jìn)入位置,FPPA 的中斷向量是各FPP 的進(jìn)入位置. 如上圖中address 0h-7h 分別為FPP#0-7 的進(jìn)入位置,address 0x10 才是“中斷副程式” 的進(jìn)入位置,故其程式寫(xiě)法如下
FPPA 指令介紹 (Instructions Set)
| FPPA Instructions Set | |
| Data Transfer Instructions (16) | |
| Instruction | Function |
| mov a,I | Move immediate data to ACC。 |
| mov M,a | Move data from ACC to memory |
| mov a,M | Move data from memory to ACC |
| mov a,IO | Move data from IO to ACC |
| mov IO,a | Move data from ACC to IO |
| pushw index | Move the content of index to be the content of stack pointer |
| pushw pcN | Move the content of program counter of Nth FPP unit to be the content of stack pointer |
| popw index | Restore the content of stack pointer to be the content of index |
| popw pcN | Restore the content of stack pointer to be the content of program counter of the Nth FPP unit |
| ldtabh index | Load high byte data in OPT to ACC by using index as OPT address |
| ldtabl index | Load low byte data in OTP to ACC by using index as OTP address |
| ldt16 index | Move 16-bit counting values in Timer16 to memory which is addressed by index |
| stt16 index | Store 16-bit data from memory addressed by index to Timer16 |
| idxm a,index | Move data from specified memory to ACC by indirect method |
| idxm index,a | Move data ACC to specified memory by indirect method |
| xch M | Exchange data between ACC and memory |
| Arithmetic Operation Instructin (20) | |
| add a,I | Add immediate data with ACC, then put result in ACC |
| add a,M | Add data in memory with ACC, then put result in ACC |
| add M,a | Add data in memory with ACC, then put result in ACC |
| addc a,M | Add data in memory with ACC and carry bit, then put result in ACC |
| addc M,a | Add data in memory with ACC and carry bit, then put result in memory |
| addc a | Add carry with ACC, then put result in ACC |
| addc M | Add carry with memory, then put result in memory |
| nadd a,M | Add negative logic (2's complement) of ACC with memory |
| nadd M,a | Add negative logic (2's complement) of memory with ACC |
| sub A,I | Subtraction immediate data from ACC, then put result in ACC. |
| sub a,M | Subtraction data in memory from ACC, then put result in ACC. |
| sub M,a | Subtraction data in ACC from memory, then put result in memory |
| subc a,M | Subtraction data in memory and carry from ACC, then put result in ACC |
| subc M,a | Subtraction ACC and carry bit from memory, then put result in memory |
| subc a | Subtraction carry from ACC, then put result in ACC |
| subc M | Subtraction carry from the content of memory, then put result in memory |
| inc M | increment the content of memory |
| dec M | Decrement the content of memory |
| clear M | Clear the content of memory |
| mul | Multiplication operation. An 8x8 unsigned multiplication will be executed. |
| Shift Operation Instructions (11) | |
| sr a | Shift right of ACC |
| src a | Shift right of ACC with carry |
| sr M | Shift right the content of memory |
| src M | Shift right of memory with carry |
| sl a | Shift left of ACC |
| slc a | shift left of ACC with carry |
| sl M | Shift left of memory |
| slc M | Shift left of memory with carry |
| swap a | Swap the high nibble and low nibble of ACC |
| swap M | Swap th high nibble and low nibble of memory |
| Logic Operation Instructions (16) | |
| and a,I | Per logic AND on ACC and immediate data, then put result in ACC |
| and A,M | Per logic AND on ACC and memory, then put result in ACC |
| and M,a | Per logic AND on ACC and memory, then put result in memory |
| or a,I | Per logic OR on ACC and immediate data, then put result in ACC |
| or a,M | Per logic OR on ACC and memory, then put result in ACC |
| or M,a | Per logic OR on ACC and memory, then put result in memory |
| xor a,I | Per logic XOR on ACC and immediate data, then put result in ACC |
| xor a,M | Per logic XOR on ACC and memory, then put result in ACC |
| xor M,a | Per logic XOR on ACC and memory, then put result in memory |
| not a | Per 1's complement (logical complement) of ACC |
| not Mry | Per 1's complement (logical complement) of memo |
| neg a | Per 2's complement of ACC |
| neg M | Per 2's complement of memory |
| comp a,I | Compare ACC with immediate data |
| comp a,M | Compare ACC with the content of memory |
| comp M,a | Compare ACC with the content of memory |
| Operation Instructions (6) | |
| set0 IO.n | Set bit n of IO port to low |
| set1 IO.n | Set bit n of IO port to high |
| tog IO.n | Toggle bit state of bit n of IO port |
| set0 M.n | Set bit n of memory to low |
| set1 M.n | Set bit n of memory to high |
| swapc IO.n | Swap the n-th bit of IO port with carry bit |
| Conditonal Operation Instructions (13) | |
| ceqsn a,I | Compare ACC with immediate data and skip next instruction if both are equal |
| ceqsn a,M | Compare ACC with memory and skip next instruction if both are equal |
| cesn M,a | Compare ACC with memory and skip next instruction if both are equal |
| t0sn IO.n | Check IO bit and skip next instruction if it's low |
| t1sn IO.n | Check IO bit and skip next instruction if it's high |
| t0sn M,n | Check memory bit and skip next instruction if it's low |
| t1sn M,n | Check memory bit and skip next instruction if it's high |
| izsn a | increment ACC and skip next instruction if ACC is zero |
| dzsn a | Decrement ACC and skip next instruction if ACC is zero |
| izsn M | Increment memory and skip next instruction if memory is zero |
| dzsn M | Decrement memory and skip next instruction if memory is zero |
| wait0 IO.n | Go next instruction until bit n of IO power is low; otherwise, wait here |
| wait1 IO.n | Go next instruction until bit n of IO power is high; otherwise, wait here |
- FPPA 共有97 個(gè)(不同系列,指令略有增減)1T RISC type 功能強(qiáng)大的指令.大部分的指令看datasheet 就知道其用法,不再多敘,這里只介紹比較容易引起誤解,或datasheet 敘述不 容易理解的地方特別提出說(shuō)明
wait0,wait1: 只能針對(duì)I/O 或register “gdio”,但不能對(duì)記憶體, 其功能如流程圖所示,一直要等到I/O 或gdio.x =0 或1 成立才往下繼續(xù)執(zhí)行 ,因傳統(tǒng)的MCU,只有一顆MCU,故無(wú)法去實(shí)現(xiàn)這種指令,否則如果條件不成立,程式就一直停在那,形同“當(dāng)機(jī)”.
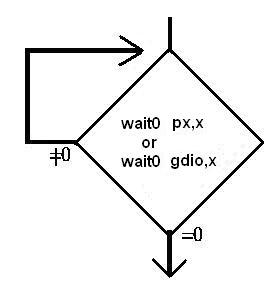
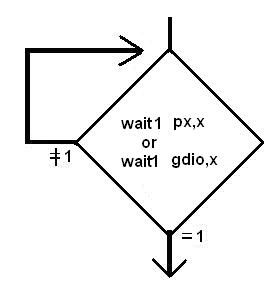
delay :直接delay x 個(gè)system clock 才往下繼續(xù)執(zhí)行, 例如system clock = 8Mhz,pmode = 0,FPP#0 執(zhí)行“delay 100” =100*1/4M = 25us,但FPPA#1執(zhí)行“delay 100” = 100 * 1/1M = 100us.
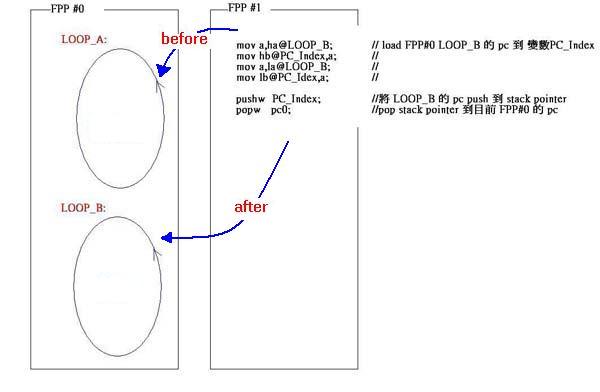
pushw,popw: push & pop 程式指標(biāo)
由于PFPA 是一顆8 核心的MCU,不同MCU 間可更改彼此的程式指標(biāo)“pc”, 來(lái)達(dá)到強(qiáng)迫其他MCU 去執(zhí)行某段程式的路徑之目的,但要小心運(yùn)用,否則容易破壞程式的結(jié)構(gòu). 下例中的FPP#0 原本只會(huì)在LOOP_A無(wú)窮的回圈中打轉(zhuǎn), FPP#1 經(jīng)由“pushw” 和“popw” 改變了FPP#0 的程式指標(biāo), 讓FPP#0 變?cè)贚OOP_B無(wú)窮回圈中 打轉(zhuǎn).
臺(tái)灣應(yīng)廣科技的杰出創(chuàng)始人唐總、銷售總部的領(lǐng)航者李總以及業(yè)務(wù)部門(mén)的精英劉總近日親臨我司,與我們團(tuán)隊(duì)展開(kāi)了一場(chǎng)深入且富有成果的交流。在這次會(huì)晤中,我們深入探討了當(dāng)前芯片銷售與推廣領(lǐng)域的挑戰(zhàn)與機(jī)遇,以及各級(jí)代理商在市場(chǎng)中面臨的具體需求和挑戰(zhàn)。
唐總以其豐富的行業(yè)經(jīng)驗(yàn)和前瞻性的視野,為我們揭示了科技發(fā)展的最新趨勢(shì)和市場(chǎng)變化。他強(qiáng)調(diào),隨著技術(shù)的日新月異和市場(chǎng)競(jìng)爭(zhēng)的日益激烈,代理商在芯片銷售與推廣過(guò)程中需要不斷創(chuàng)新,緊跟市場(chǎng)脈搏,靈活調(diào)整策略,以滿足客戶多樣化的需求。